As the Russia-Ukraine war continues, its impact on global trade has grown more severe, affecting critical industries such as energy, agriculture, and manufacturing. Disrupted supply chains have resulted in delayed shipments and increased costs for businesses worldwide. Countries dependent on Ukrainian and Russian exports, especially in Europe, have faced rising prices and shortages of essential goods. The global impact of the Russia-Ukraine war is expected to persist, reshaping trade policies and economic strategies for years to come.
Introduction
The global trade landscape has been significantly altered by the Russia – Ukraine war, as economies around the world struggle to adjust to the shifting geopolitical dynamics. The conflict has not only caused immediate economic disruptions but has also introduced long-term uncertainties for global markets, particularly in terms of energy, food supplies, and commerce. Understanding these impacts is crucial for anticipating the future trajectory of the world economy in the wake of the war.
Overview of the Conflict
The Russia – Ukraine war began with Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022, sparking a conflict that has since persisted and intensified. The geopolitical tensions that arose from this war have created volatility in global markets, with trade, energy supplies, and economic growth all affected. The impact of the Russia – Ukraine war is particularly evident in sectors like energy and agriculture, where both nations play critical roles as exporters.
Significance to Global Trade
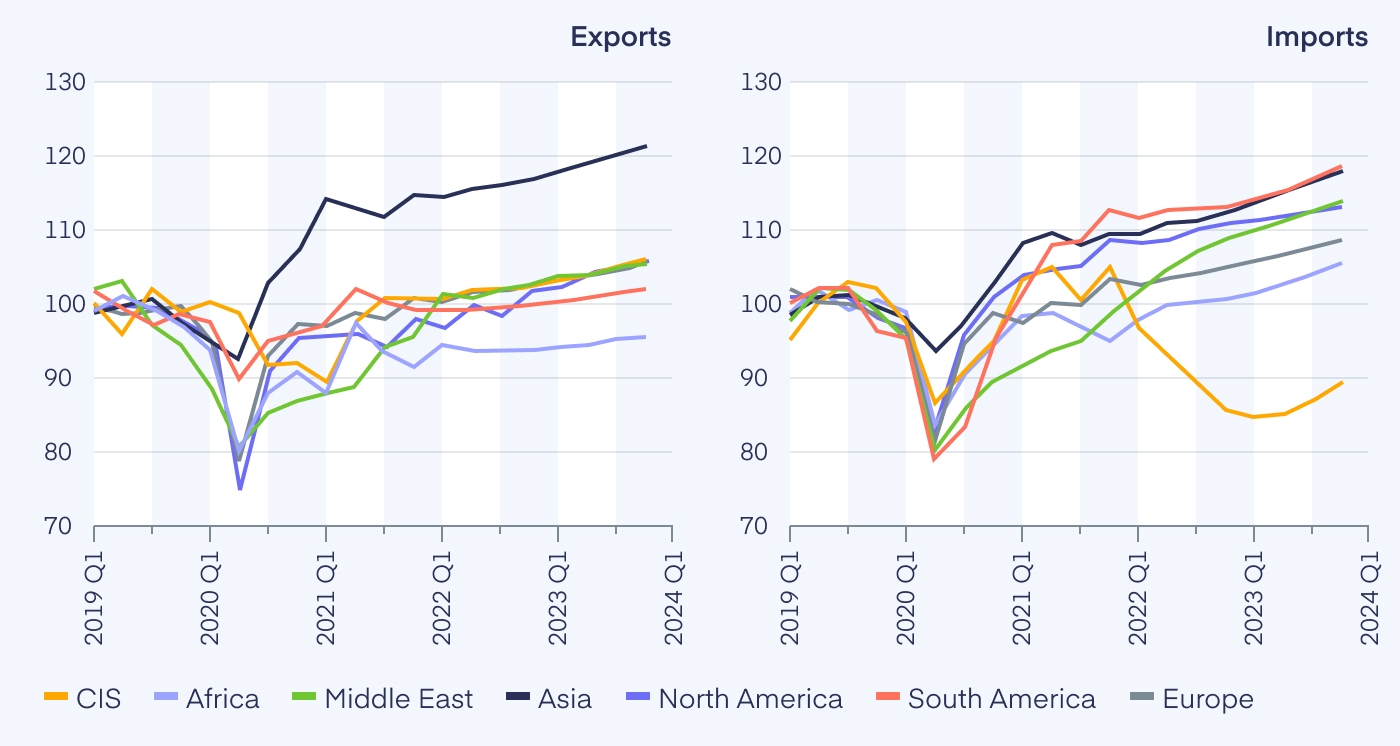
The global impact of the russia ukraine war has been felt in the form of disrupted supply chains, increased commodity prices, and a slowdown in international trade. Russia’s aggression has led to sanctions that have restricted its ability to trade with many Western nations, further destabilizing global markets. Ukraine, a major exporter of grain, has seen its trade routes blocked, which has sent shockwaves through global food markets. As a result, the impact of the Russia-Ukraine war on the world economy continues to grow, influencing trade policies and global economic strategies.
Russia-Ukraine War Threatens Recovery of Global Economy
The Russia – Ukraine war has jeopardized the already fragile recovery of the global economy, which was attempting to rebound from the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. The conflict has not only disrupted the supply of essential resources but also triggered inflationary pressures and a slowdown in growth across major economies. These effects are particularly worrisome for nations that rely heavily on energy imports or exports.
Impact on Major Economies
The impact of the russia ukraine war on major economies has been profound. Several key effects include:
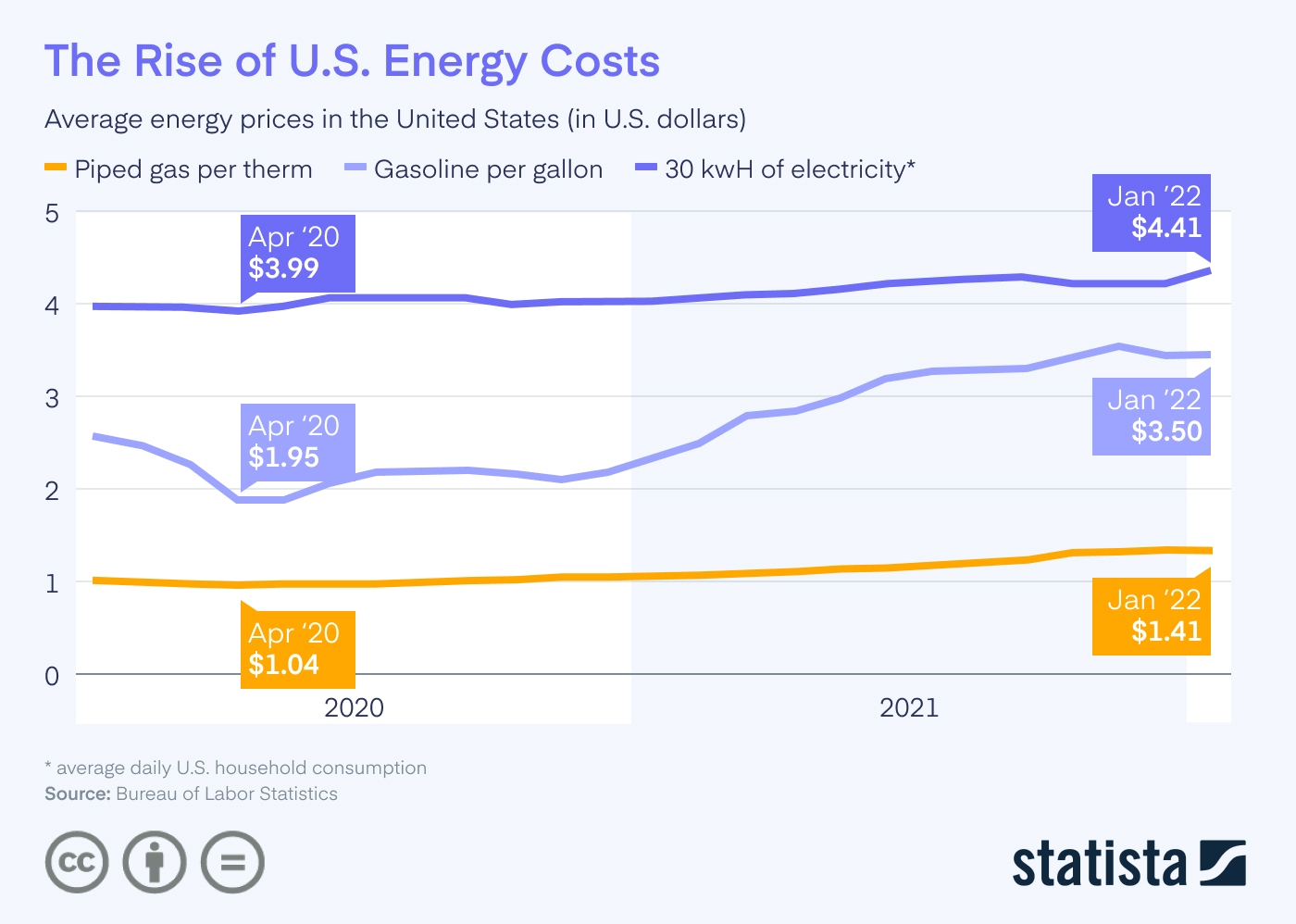
- Energy price hikes: Countries in Europe, especially Germany and France, have experienced significant fuel shortages and rising energy costs.
- Inflation spikes: Higher prices for energy and commodities are driving inflation across the globe, including in the U.S. and EU.
- Slowed industrial output: Industries that rely on raw materials from Russia or Ukraine have been forced to slow down due to supply shortages.
- Financial market volatility: Stock markets in major economies have seen increased fluctuations in response to the impact of the Russia-Ukraine war.
Long-term Economic Forecasts
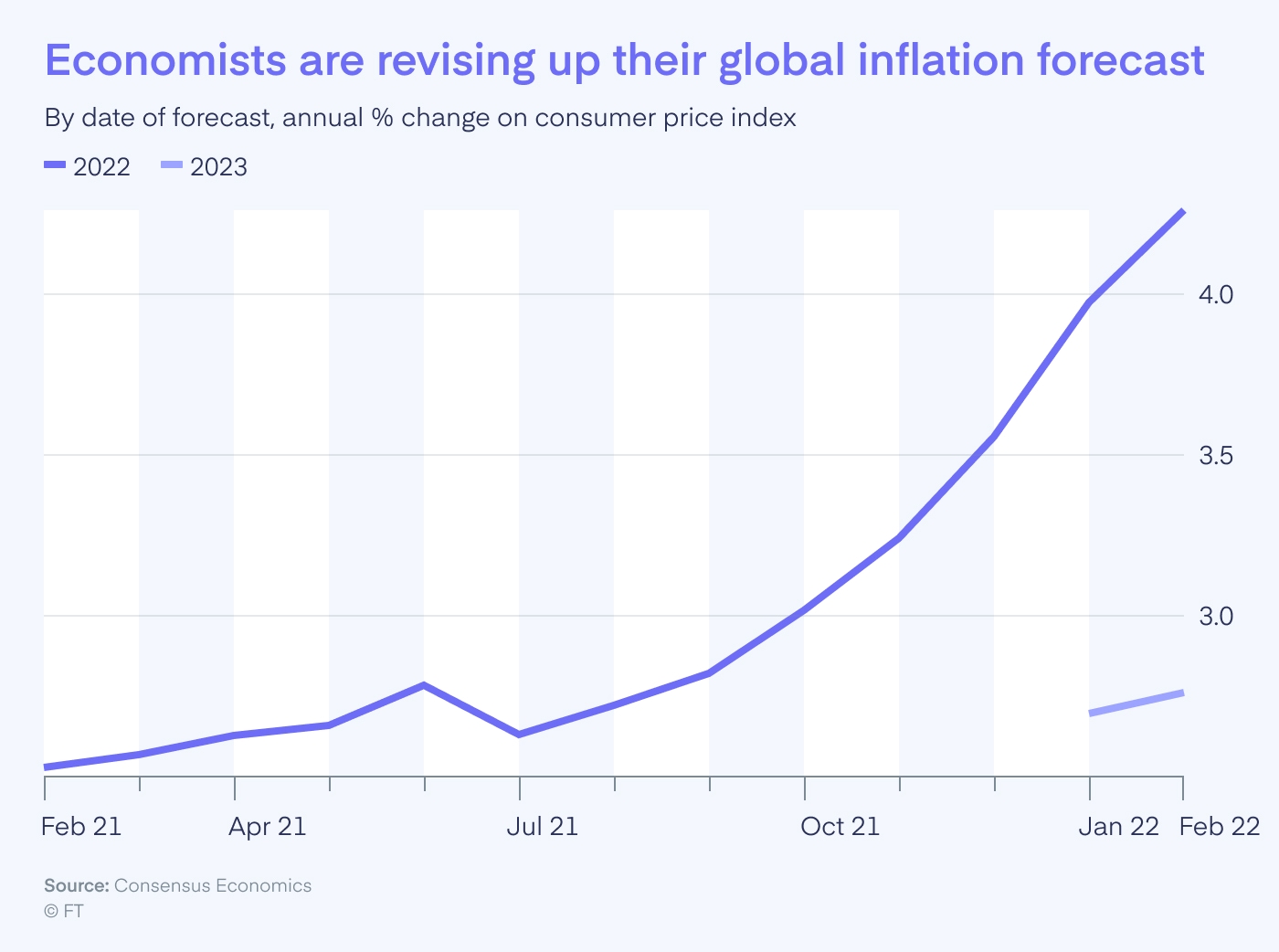
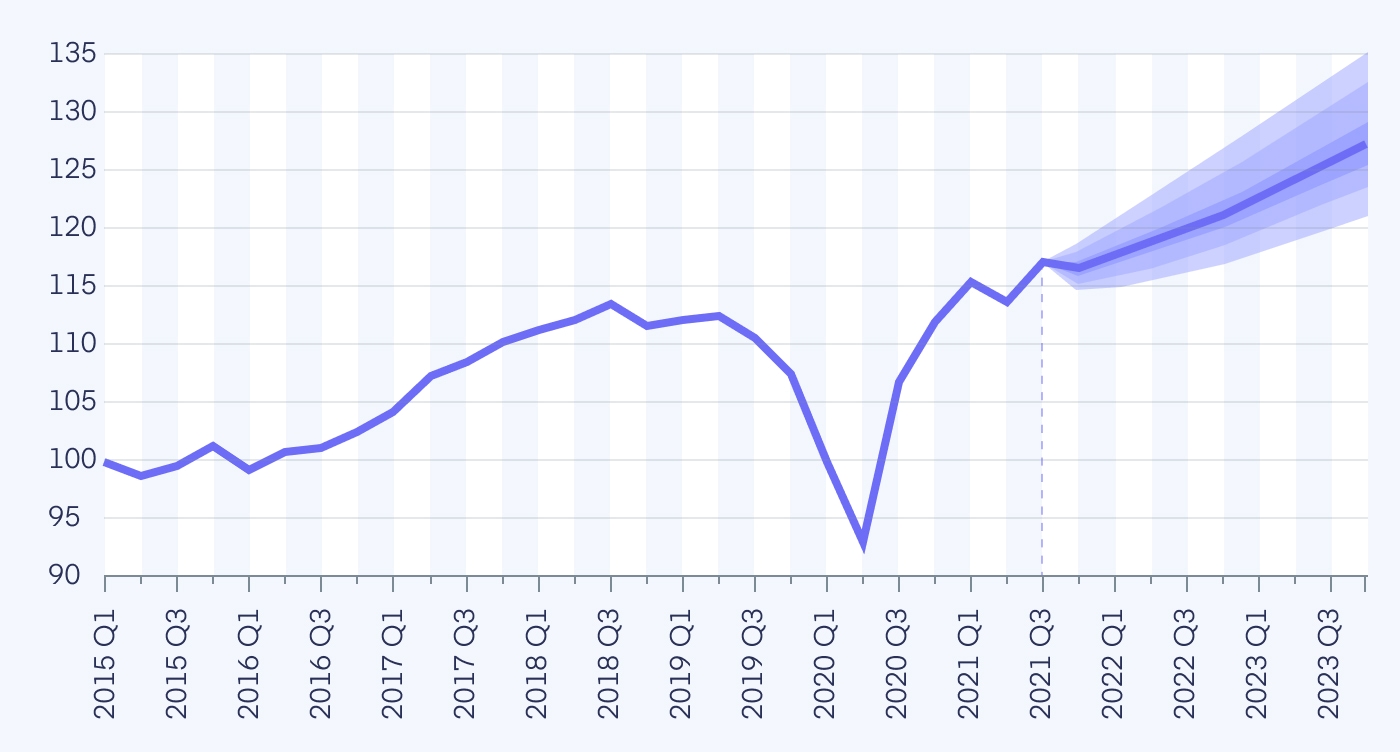
Economists have revised their global forecasts due to the impact of the Russia – Ukraine war. The World Bank and IMF have downgraded growth predictions for 2022 and beyond, citing the uncertainty and ongoing disruptions caused by the war. These institutions warn that the long-term consequences of the conflict will likely lead to slower economic growth and continued inflationary pressures. The economic impact of russia ukraine war may also force central banks to take more aggressive measures, such as raising interest rates to control inflation, which could stifle future growth.
The Economic Impacts of The Ukraine Crisis on Global Trade
The Russia – Ukraine war has disrupted global trade on an unprecedented scale. Both Russia and Ukraine are significant players in global markets for energy, metals, and food. As the war drags on, supply chain disruptions, changes in trade policies, and sanctions have exacerbated the global trade crisis. These factors have particularly affected low-income countries that rely heavily on imports from the region.
Disruptions in Supply Chains
One of the most significant impacts of the russia ukraine war on international trade has been the severe disruption to global supply chains. The war has affected everything from agricultural exports to the transport of raw materials, as key routes through Ukraine have been blocked or destroyed. The impact of war between Russia and Ukraine has led to delayed shipments, higher costs, and reduced availability of goods, creating further economic strain on countries dependent on these supply chains.
Changes in Trade Policies and Sanctions
The war has also led to sweeping changes in global trade policies. As nations impose sanctions on Russia, the impact of the Russia – Ukraine war on international trade has become more pronounced. Sanctions have reduced Russia’s ability to engage in global commerce, particularly in sectors like oil, gas, and metals, which are critical to the global economy. This has created new challenges for countries trying to maintain stable trade relationships, as they seek alternatives to Russian goods.
Unveiling Food and Fuel Crises
The Russia – Ukraine war has sparked both a food crisis and a fuel crisis, as the conflict disrupts critical supplies of grain and energy. The war has driven up food prices and caused fuel shortages, particularly in Europe, where countries rely heavily on Russian natural gas. As the war continues, these crises are expected to worsen, further impacting global trade and economic stability.
Escalation of Food Prices
The impact of the russia ukraine war on food prices has been especially severe. Ukraine, a major global exporter of grain, has been unable to maintain its usual production and export levels, leading to shortages and skyrocketing prices worldwide. The global impact of the russia ukraine war is felt most acutely in developing countries, where food insecurity has worsened due to rising costs. These price increases are compounded by supply chain disruptions and the inability of nations to access affordable food imports.
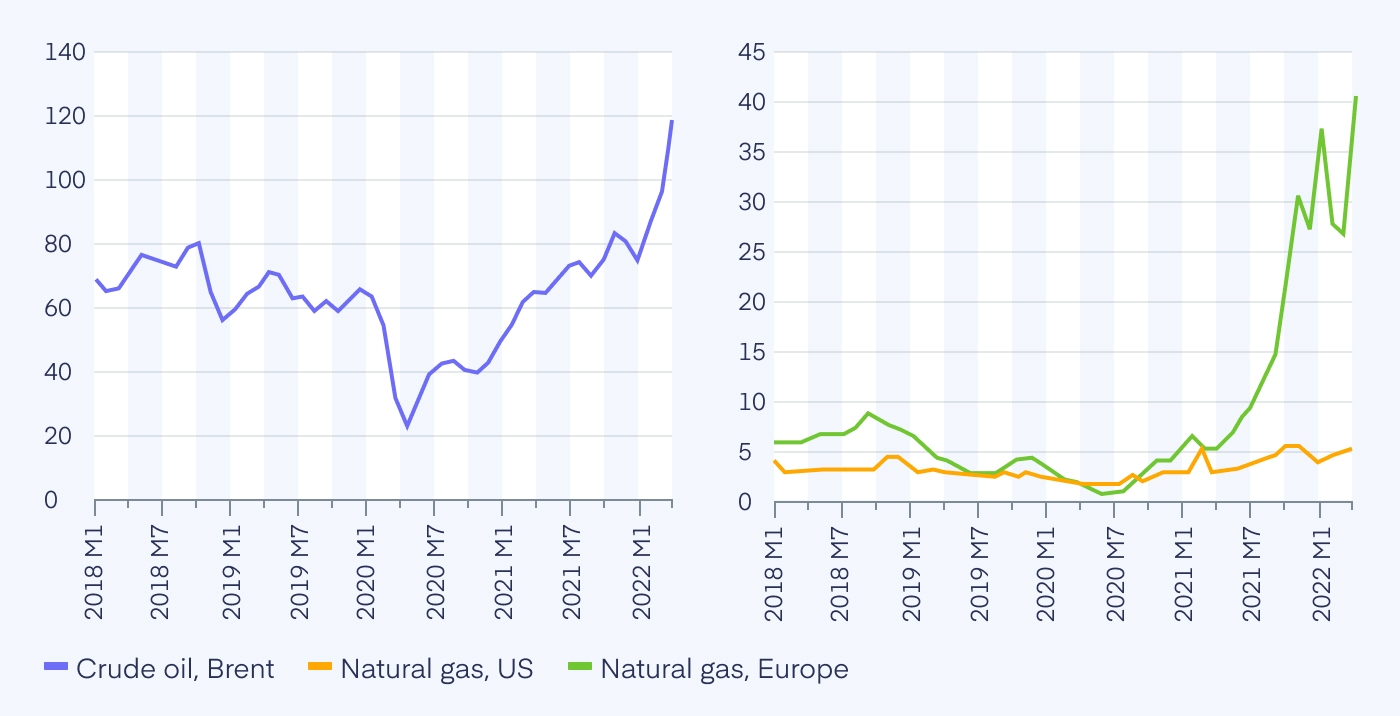
Fuel Supply Disruptions and Energy Security
The energy sector has been particularly vulnerable to the impact of the Russia – Ukraine war. As countries in Europe try to reduce their reliance on Russian natural gas, fuel prices have surged globally. The economic impact of the russia-ukraine war on energy markets is profound, with natural gas prices in Europe soaring and oil prices fluctuating. This volatility has created uncertainty in the global energy market, forcing countries to seek alternative sources and reevaluate their energy security strategies.
Global eCommerce Restraints
The Russia – Ukraine war has also severely impacted the global eCommerce landscape. With supply chain disruptions and increased shipping costs, cross-border eCommerce has become more challenging. As global trade slows down, eCommerce platforms are forced to adapt to new realities, including changing consumer demand and higher operational costs.
Impact on Cross-border eCommerce
The impact of the russia ukraine war on cross-border eCommerce has been significant. The war has caused shipping delays, increased transportation costs, and led to product shortages, all of which have affected the ability of businesses to deliver goods on time. Many small and medium-sized enterprises that rely on international trade have been hit particularly hard, as the rising costs and uncertainty make it difficult to maintain profitability.
Adaptations by Global eCommerce Platforms
In response to the impact of the Russia – Ukraine war, global eCommerce platforms have been forced to adapt quickly. Companies are reevaluating their supply chains, investing in local production, and finding alternative suppliers to mitigate the effects of the war. Additionally, eCommerce businesses are implementing strategies to address changing consumer behaviors, as many customers have reduced spending due to the economic uncertainty caused by the war.
Final Word
The Russia-Ukraine war has created unprecedented challenges for global trade, economies, and industries. The conflict has disrupted global supply chains, increased energy and food prices, and destabilized markets, leaving governments and businesses grappling with the long-term effects. While the full impact of the russia ukraine war is still unfolding, its consequences are already being felt worldwide, and it is evident that the conflict will have lasting repercussions on the global economy. Trade disruptions, rising costs, and ongoing geopolitical instability will continue to shape economic forecasts for the foreseeable future.
As the war persists, businesses and governments must adapt to this evolving landscape to minimize its negative impact on global trade and commerce. This requires rethinking supply chain strategies, exploring alternative markets, and adopting more resilient business models. At Profit Whales, we are committed to helping companies navigate these challenges by providing expert guidance and strategies to optimize their Amazon operations. For more information on how we can assist your business in adapting to the current economic climate, feel free to contact us. Together, we can build a path toward sustainable growth, even in uncertain times.
FAQ
What types of economic sanctions have been implemented, and how do they affect global trade?
Sanctions against Russia include restrictions on energy exports, financial transactions, and trade in key industries. These measures have had a significant impact on global trade by reducing the availability of key resources and driving up prices.
In what ways have food prices been affected globally by the war?
The Russia – Ukraine war has disrupted Ukraine’s grain exports, leading to a global increase in food prices. Many developing countries have been especially affected by these price hikes.
How is the energy sector coping with disruptions due to the war?
The impact of the Russia – Ukraine war on the energy sector has led to rising prices and supply shortages, particularly in Europe. Countries are seeking alternative energy sources and rethinking their energy policies to ensure security.
What are the immediate effects of the war on cross-border eCommerce?
The war has caused significant disruptions in supply chains, leading to delays and increased costs for cross-border eCommerce. Businesses have been forced to adapt by finding new suppliers and adjusting shipping methods.
What measures are eCommerce platforms taking to adapt to the new trade environment?
Ecommerce platforms are adapting to the impact of the Russia-Ukraine war by diversifying their supply chains, investing in local production, and adjusting to changes in consumer demand. These efforts are aimed at minimizing disruptions and maintaining service continuity.